 Magazine
Magazine
Food defence is the effort to protect food from intentional acts of adulteration intended to cause harm to the public. Companies make all possible efforts to significantly minimize or prevent intentional adulteration event.
Intentional adulteration is the deliberate contamination of food with a biological, chemical, radiological, or physical agent by an individual or group of individuals with the intent of causing harm to public health.
In order to prevent this, facilities develop and implement a food defence plan. This is a fundamental step towards an effective food defence program.
Most of the time companies misinterpret vulnerable assessment with Food Defence. A vulnerable assessment is a systematic assessment of points, steps, or procedures to identify and rank vulnerabilities to intentional adulteration.
After the establishment identifies potential vulnerabilities, it will then examine possible mitigation strategies such as the use of physical security (e.g., closed circuit TV, alarms, doors, guards, access control systems), personnel security (e.g., background checks, coloured hats, screening, training, awareness) or procedural security (e.g., key control, having two persons present when raw materials are accessed, testing).
It is important to perform a vulnerability assessment using appropriate methods and qualified individual(s). In addition to that it is also necessary to Identify actionable process steps for significant vulnerabilities.
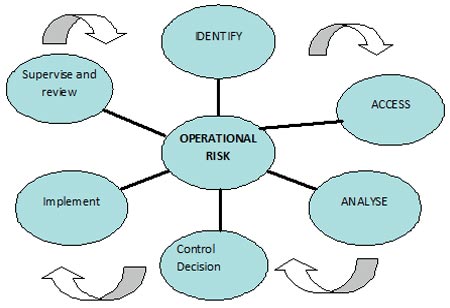
I have an IAACIR method to identify such operational risks.
For Example:
In case of liquid storage and handling when a bulk liquid is contained in storage tanks or silos or other types of intermediate processing tanks.
The steps may include:
A) Introduction into the product stream or prior to loading for outbound shipping, Bulk or non-bulk tanks can be used to store liquid ingredients, hold liquid product for sample testing and other quality control activity, or to control flow rates of liquid ingredients or product through the production system.
B) Handling tanks also include tanks or totes where the tamper-evident seals are opened and the container itself is used for holding. At these steps, there is a high probability of mixing due to agitation which would likely cause even dispersion of a contaminant.
Mitigation Strategy Requirements includes:
1. Identify and implement mitigation strategies
2. At each Actionable Process Step
3. Must be written to explain
4. Significant vulnerability is minimized or prevented
It should also include Elements of monitoring. That is how often will the monitoring be conducted; who will conduct the monitoring event; how will the monitoring be accomplished; and what will be monitored.
Appropriate corrective action required according to the nature of the actionable process step and the nature of the mitigation strategy. And verification to demonstrate monitoring is conducted as intended; corrective actions are conducted appropriately; mitigation strategies significantly reduce or prevent vulnerabilities; review monitoring and corrective action records; re-analysis of the Food Defence Plan.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Read more...